Dental bearings are precision-engineered components inside high-speed dental handpieces that reduce friction and ensure smooth operation. Choosing the right type of bearing affects performance, longevity, and patient comfort, while also minimizing maintenance and replacement costs. Understanding these differences between dental bearings is crucial for optimizing efficiency and enhancing practice outcomes.
Types of Dental Bearings
Smooth dental bearings are designed to minimize friction, offering quiet operation during dental procedures. They are commonly found in various high-speed dental handpieces and are designed for reliability.
Common Types:
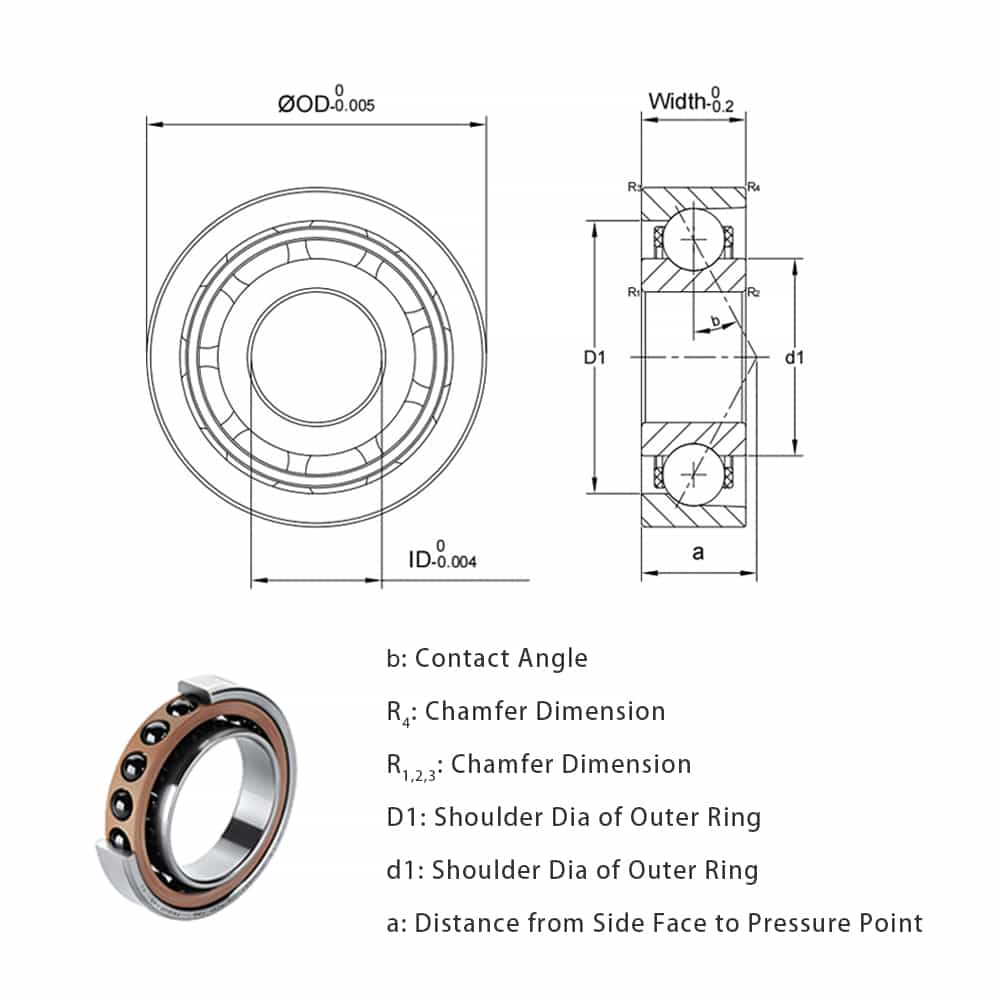
Radial ball bearings: These bearings handle loads that are perpendicular to the shaft.
Angular contact ball bearings: These are designed to support both axial and radial loads but from one direction.
Advantages:
Reliable Performance: Smooth bearings ensure dependable performance in standard dental procedures.
Quiet Operation: Low noise levels make these bearings ideal for enhancing patient comfort.

Smooth Dental Bearing - SR144K1TLZWN
Flanged bearings come with a flange on one side, making them easy to mount and secure. They are capable of supporting both radial and axial loads.
Applications:
These bearings are typically used in dental practices that need more complex handpiece configurations with secure mounting.
Advantages:
Enhanced Stability: The flange ensures the bearing stays in place, preventing movement during operations.
Precise Operation: Ideal for demanding dental procedures requiring precision.
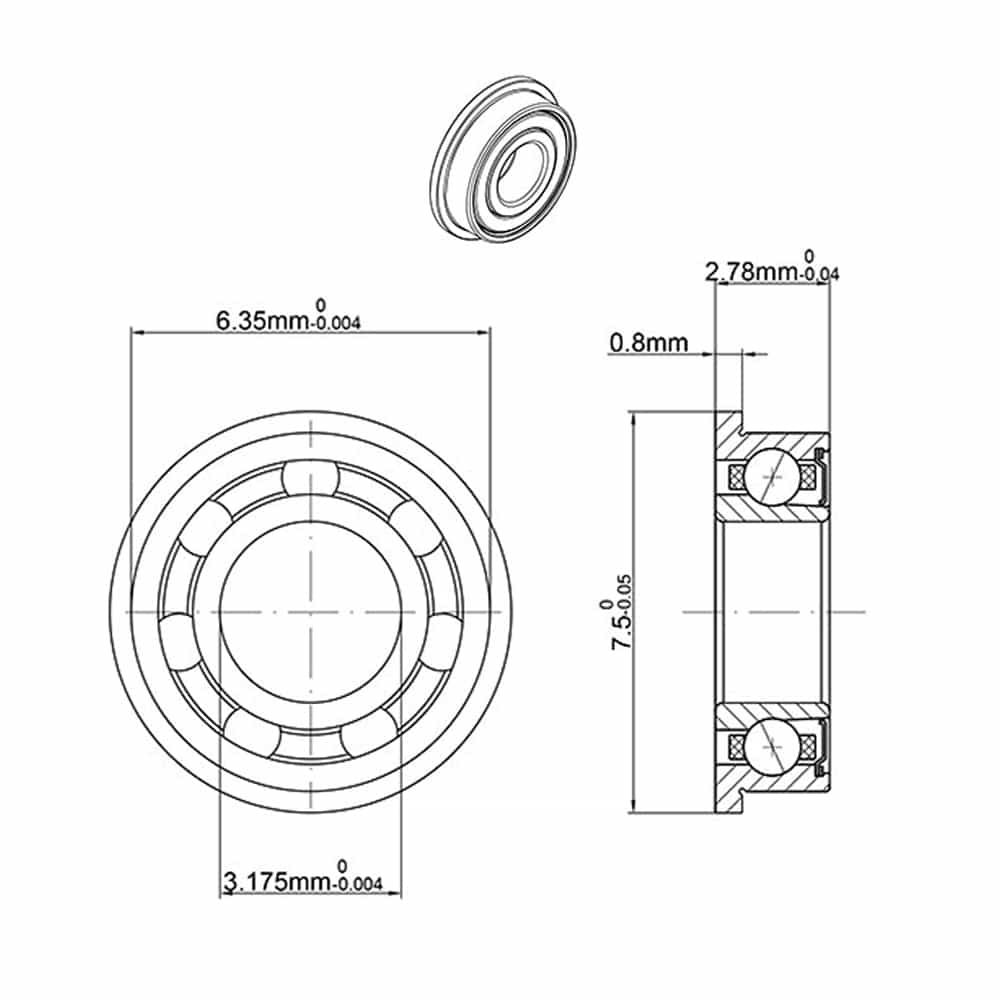
Flanged Dental Bearing - SFR144K1TLZW
Stepped bearings have multiple diameters to allow for precise alignment, making them suitable for dental handpieces that use varying shaft sizes.
Applications:
Ideal for handpieces with different components that require specific bearing diameters for smooth operation.
Advantages:
Optimal Performance: These bearings ensure the handpiece operates efficiently, even with varying shaft sizes.
Versatility: They adapt well to different designs of dental handpieces.
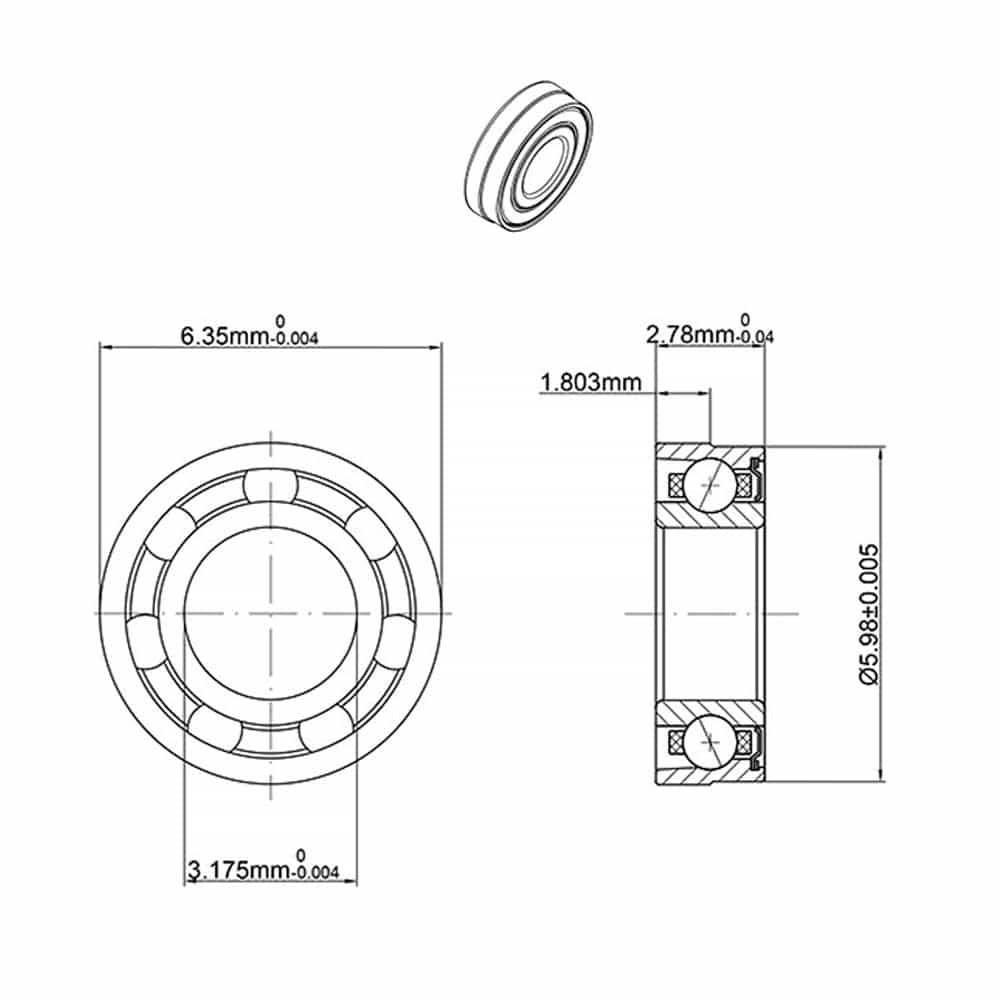
Stepped Dental Bearing - SR144K2TLKZWN
Unique bearings are specially designed for specific dental applications, often custom-made to meet the needs of specialized dental procedures.
Applications:
These bearings are used in specialized or complex procedures where standard bearings may not be sufficient.
Advantages:
Tailored Solutions: Unique bearings offer customized solutions for specific dental applications, ensuring high performance.
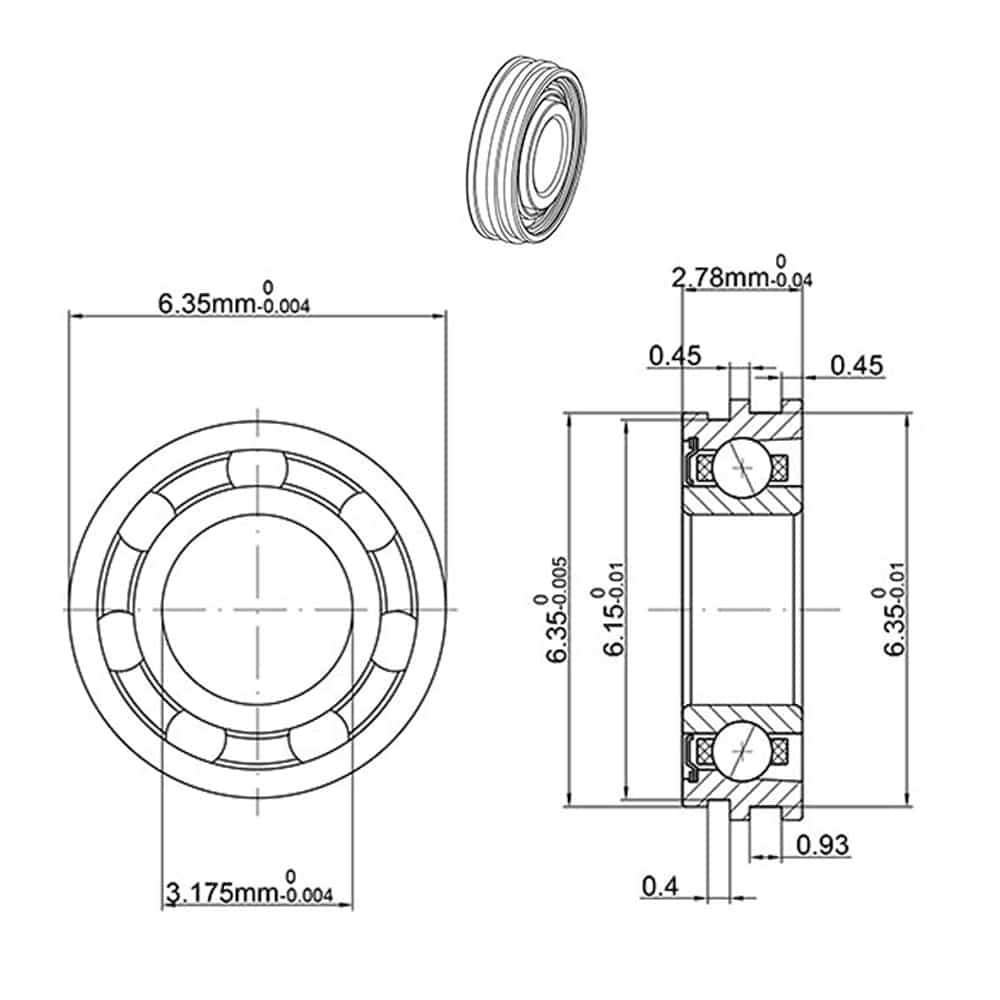
Unique Dental Bearing - SFFR144K2TLGZWN
Steel ball bearings are made from stainless steel and are known for their durability. They are affordable and can handle significant wear and tear but require regular lubrication.
Applications:
These stainless steel bearings are suitable for general-purpose handpieces, especially where cost effectiveness is a priority.
Pros:
Cost effective and widely available.
Suitable for standard dental procedures.
Cons:
Requires regular lubrication and maintenance free periods are shorter.
Produces more noise than other materials.

Ceramic bearings, especially those made from silicon nitride or ceramic balls, offer superior heat resistance and lower friction compared to steel bearings. They also have a longer lifespan and operate more quietly.
Applications: High-speed dental handpieces benefit greatly from ceramic bearings due to their efficiency and durability at high speeds.
Pros:
Reduced friction and quieter operation.
Longer lifespan, resulting in fewer replacements.
Cons: Higher initial cost than steel bearings.
Hybrid ceramic bearings combine ceramic balls with steel ball bearings or steel races. This blend provides a balance between performance and durability.
Applications: Ideal for dental professionals looking for enhanced performance with moderate maintenance needs.
Pros:
Smoother operation and longer lifespan than all-steel bearings.
Less need for frequent lubrication.
Cons: May still require periodic maintenance, though less frequently than steel bearings.
Radial bearings feature a crown retainer and are easier to install compared to angular contact bearings. They handle radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft) and can support axial loads from both sides.
Applications: Ideal for dental practices using handpieces that experience loads from multiple directions.
Pros: Easier to install and maintain.
Cons: Not as efficient at high speeds as angular contact bearings
Angular contact ball bearings have a full retainer and are designed for high-speed operations. These bearings are specifically built to handle axial loads from one direction, making them suitable for precision work.
Applications: These bearings excel in high-speed dental handpieces, especially those requiring high precision.
Pros: Longer lifespan and better performance at high speeds.
Cons: More complex to install and can only handle axial loads from one direction.
Open bearings have no seals, allowing them to operate at maximum speed. However, they are more prone to contamination and require frequent cleaning and lubrication.
Pros: Maximum speed capacity.
Cons: Prone to contamination and requires more maintenance.
Shielded bearings come with single or double shields that protect against dust and other contaminants. This makes them better suited for handpieces that undergo frequent sterilization.
Pros: Protection against external contamination.
Cons: Slightly slower performance due to the shields.
High quality bearings, whether lube free bearings or those requiring lubrication, need regular care to maintain optimal performance. Proper cleaning, lubrication, and handling will help reduce wear and tear, keeping the handpieces in good condition and extending their lifespan.
Best Practices
Cleaning: Regularly clean the handpiece to avoid debris buildup.
Lubrication: Apply the recommended amount of lubrication based on the bearing type.
Handling: Handle handpieces with care to avoid premature damage to the bearings.
Good maintenance practices help reduce friction, noise, and vibration in your high-speed dental handpieces, which in turn leads to better patient experiences and lower repair costs for your practice.